[Second Update, 20 November 2023: Comments received via email from another reader, Nelson Sollenberger, KA2C, made some interesting points. I'm including these in this blogpost, as they counter some of OX2AXE's points assumptions of mine.]
In this fourth post I thought I'd look into relays. (Part 3 of this series can be found here).
I noticed that Elecraft uses the Omron G2RL series in their KAT-500. The "high capacity" version of this family (which they use) is spec'd at 16 amps.
Looking at the Digikey website for other high-current low-profile relays, I found one made by Panasonic (their ALZ family). Coincidentally, it has the same specs as the Omron relay.
So that I could compare them, I ordered a few of the Omron and the Panasonic relays from Digikey. Here are some photos...
Omron G2RL relays on the left, Panasonic ALZ relays on the right, all with covers removed.
Omron G2RL-14-E Relay, view of contact mechanism. Note the width of the copper:
Omron Relay, normally-open contacts forced closed (12VDC applied):
Looks pretty good!
Panasonic ALZ12B12 Relay, normally-open contacts forced closed:
Hmmmm.....It looks like the contacts aren't contacting center-to-center, but rather at their top. Personally, I prefer the Omron relay -- it looks like it the relay contacts connect at their centers.
Looking more closely at the Omron Relay specs...
The important Omron Relay Specs:
Let's check that this breakdown voltage is OK for my tuner application...
At low frequencies (e.g. 50/60 Hz), the breakdown voltage is 440 VAC. But for HF RF signals the breakdown voltage is lower. [K6JCA update -- this is the wrong voltage to use. I correct this just a bit further down this post.]
Per the image below (from Nautel's "Recommendations for Transmitter Site Preparation, Sept., 04", available here), for the frequencies that interest me, the breakdown voltage is about 0.8 times the low-frequency AC breakdown.
Given this relationship, the RF breakdown voltage would be equal to 0.8 * 440 Vrms (about 350 Vrms, or about 500 Vpk). K6JCA update -- this is not correct...
In this fourth post I thought I'd look into relays. (Part 3 of this series can be found here).
I noticed that Elecraft uses the Omron G2RL series in their KAT-500. The "high capacity" version of this family (which they use) is spec'd at 16 amps.
Looking at the Digikey website for other high-current low-profile relays, I found one made by Panasonic (their ALZ family). Coincidentally, it has the same specs as the Omron relay.
So that I could compare them, I ordered a few of the Omron and the Panasonic relays from Digikey. Here are some photos...
Omron G2RL relays on the left, Panasonic ALZ relays on the right, all with covers removed.
Omron G2RL-14-E Relay, view of contact mechanism. Note the width of the copper:
Omron Relay, normally-open contacts forced closed (12VDC applied):
Looks pretty good!
Panasonic ALZ12B12 Relay, normally-open contacts forced closed:
Hmmmm.....It looks like the contacts aren't contacting center-to-center, but rather at their top. Personally, I prefer the Omron relay -- it looks like it the relay contacts connect at their centers.
Looking more closely at the Omron Relay specs...
The important Omron Relay Specs:
- Contact Material: Ag-alloy (Cd Free). (Note that an earlier datasheet states AgSnO2 for single-pole relays; AgNi for double-pole relays).
- Contact Resistance: 100 milliohms, max.
- Operating Current: 16A
- Max Switching Voltage: 440VAC, 300VDC. (I'm confused as to why the AC voltage is higher than the DC voltage -- I would think that the DC voltage would be Vpk of the AC, or about 600 volts.) [Comment from OH2AXE (20 June 16): they are like this because DC arcs easier than AC when contact opens with full load (ref. welding). These are power relays intended for DC or mains frequency. RF is even worse, because it ionizes air and causes an arc easier than 50/60 Hz DC. You have noted this later in the text. ALWAYS tune with a much lower RF power and arcing should not be a problem.]
- Dielectric Strength Between Contacts "of the same polarity": 1000 VAC, 50/60Hz, 1 Minute. (I'm confused by what the meaning could be of "contacts of the same polarity", but I believe this spec is the same as Panasonic's "Breakdown voltage between open contacts.")
- [Comment from OH2AXE (20 June 16): This specification is valid only for relays with 2 or more "poles", in this case DPDT version. It is the breakdown voltage between two adjacent contact sets. Your assumption leads to significant errors later in your text. For HF frequencies use the DC switching voltage (300V in this case) + safety margin. You note this later ("Recommendations for Transmitter Site Preparation"). ALWAYS tune with a much lower RF power and contact breakdown (i.e. arcing over) should not be a problem.]
- [Comment from KA2C (30 Nov. 23): If the Omron specifications are compared to similar relays from other manufacturers (for example, Schrack, Zettler, or Panasonic), it becomes apparent that Omron's dielectric strength for contacts "of the same polarity" actually refers to the breakdown voltage between open contacts on the same pole. Thus, it applies to any relay; SPST, SPDT, DPDT, etc.]
At low frequencies (e.g. 50/60 Hz), the breakdown voltage is 440 VAC. But for HF RF signals the breakdown voltage is lower. [K6JCA update -- this is the wrong voltage to use. I correct this just a bit further down this post.]
Per the image below (from Nautel's "Recommendations for Transmitter Site Preparation, Sept., 04", available here), for the frequencies that interest me, the breakdown voltage is about 0.8 times the low-frequency AC breakdown.
(click on image to enlarge)
Given this relationship, the RF breakdown voltage would be equal to 0.8 * 440 Vrms (about 350 Vrms, or about 500 Vpk). K6JCA update -- this is not correct...
Note that OH2AXE (see comment section, below) recommends that the DC
breakdown value of 300 VDC be used as the RF breakdown voltage.
An emailed comment from KA2C (30 Nov 23) recommends that relay switching be done at low power levels so that arcing is not an issue. However, will the contacts arc over during actual transmissions, after tuning has been completed at a lower power?
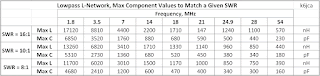
To calculate if the breakdown voltage can be exceeded if transmitting at peak power, after the Tuner has been tuned, we first calculate the "Open Contact" breakdown voltage, which, if we compare the specifications of similar relays to the Omron relay and translate Omron's "contacts of the same polarity" to the less opaque "open contacts on the same pole," is 1000 VAC,
Next, derate (for operation at RF frequencies), the 1000VAC spec by 0.8. The resulting breakdown voltage between open contacts, at RF, is therefore 800VAC [i.e. 1131 Vpeak -- K6JCA].
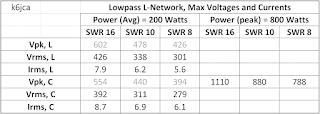
The table below shows simulated L-network voltages and currents (for an assumed a peak power level of 800 watts):
K6JCA (30 Nov. 23): Given the Vpk values in the above table for a peak transmit power of 800 watts and an SWR of 10:1, the maximum voltage across the capacitors of an L-Network is 880 Volts, peak, which is appreciably below an Omron relay's open-contact breakdown voltage at RF of 1131 Vpk. (Inductor peak voltage would be 956 Vpk, also less than the contacts' rating of 1131 Vpk).
(click on image to enlarge)
Therefore arcing during operation should not be an issue.
I made a couple of measurements on a sample-of-one G2RL-14-E relay:
Contact Resistance: 0.005 ohms (measured between the N.O. contact and the pole, with the relay energized (contacts closed), using an HP3468A DVM in 4-wire resistance measurement mode).
Contact Capacitance: 1 pF (approx) (measured between the N.O. contact and the pole, relay off, using a GenRad 1657 Digibridge).
For relay inductance, I calculate that it should be around 12 nH (Assume internal path length of 1” and contact width of 0.34” (0.87cm)).
Omron G2RL-2 DPDT Relay:
I thought I'd also take a look at the construction of the DPDT member of Omron's G2RL family, the G2RL-2:
Unlike the G2RL-14-E SPDT relay, this relay is only rated for an 8 Amp load.
Other notes on the Omron Relay:
"Sealed" seems to refer to the sealing of a tiny hole on the top of the relay package.
I really didn't see any difference between UL Class B and Class F Insulation. To me they looked the same, but I might have missed something.
With these relays and with the inductors and capacitors selected in the previous, two posts, I'll draw a preliminary schematic of the L-Network components and connections:
L-Network Schematic:
This schematic only contains the inductors, capacitors, and relay contacts. The relay magnets and other circuitry will appear in schematics later.
In its Power-Off state, the tuner defaults to Bypass Mode. That is, the capacitors are disconnected and the inductors are all shunted. There will be some parasitic effects, though, due to the capacitance of the capacitor-relays' open contacts and the inductance of the inductor-relays and the wires (or traces) interconnecting them. I'll have to see if these are an issue when I build the network.
OK -- that's it for this blog post!
The previous post in this series, Part 3, can be found here: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/06/antenna-auto-tuner-design-part-3.html
And the final "release" schematics can be found in Part 10 of this series: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2016/01/antenna-auto-tuner-design-part-10-final.html
Links to my blog posts in this Auto-tuner series:
Part 1: Preliminary Specification
Part 2: Network Capacitor Selection
Part 3: Network Inductor Selection
Part 4: Relays and L-Network Schematic (Preliminary)
Part 5: Directional Coupler Design
Part 6: Notes on Match Detection
Part 7: The Build, Phase 1
Part 8: The Build, Phase 2 (Integration of Match Detection)
Part 9: The Build, Phase 3 (Incorporating a Microcontroller)
Part 10: The Final Schematics
Resources:
My Other Tuner posts:
A quick tutorial on Smith Chart basics: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/03/a-brief-tutorial-on-smith-charts.html
The L-network: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/03/notes-on-antenna-tuners-l-network-and.html
A correction to the usual L-network design constraints: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/04/revisiting-l-network-equations-and.html
A look at highpass T-Networks: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/04/notes-on-antenna-tuners-t-network-part-1.html
More on the W8ZR EZ-Tuner: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/05/notes-on-antenna-tuners-more-on-w8zr-ez.html (Note that this tuner is also discussed in the highpass T-Network post).
The Elecraft KAT-500: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/05/notes-on-antenna-tuners-elecraft-kat500.html
The Nye-Viking MB-V-A and the Rohde Coupler : http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/05/notes-on-antenna-tuners-nye-viking-mb-v.html
Standard Caveat:
As always, I might have made a mistake in my equations, assumptions, drawings, or interpretations. If you see anything you believe to be in error or if anything is confusing, please feel free to contact me or comment below.
And so I should add -- this design and any associated information is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Relay Measurements:
Contact Resistance: 0.005 ohms (measured between the N.O. contact and the pole, with the relay energized (contacts closed), using an HP3468A DVM in 4-wire resistance measurement mode).
Contact Capacitance: 1 pF (approx) (measured between the N.O. contact and the pole, relay off, using a GenRad 1657 Digibridge).
For relay inductance, I calculate that it should be around 12 nH (Assume internal path length of 1” and contact width of 0.34” (0.87cm)).
Omron G2RL-2 DPDT Relay:
I thought I'd also take a look at the construction of the DPDT member of Omron's G2RL family, the G2RL-2:
Other notes on the Omron Relay:
"Sealed" seems to refer to the sealing of a tiny hole on the top of the relay package.
I really didn't see any difference between UL Class B and Class F Insulation. To me they looked the same, but I might have missed something.
With these relays and with the inductors and capacitors selected in the previous, two posts, I'll draw a preliminary schematic of the L-Network components and connections:
L-Network Schematic:
This schematic only contains the inductors, capacitors, and relay contacts. The relay magnets and other circuitry will appear in schematics later.
(click on image to enlarge)
In its Power-Off state, the tuner defaults to Bypass Mode. That is, the capacitors are disconnected and the inductors are all shunted. There will be some parasitic effects, though, due to the capacitance of the capacitor-relays' open contacts and the inductance of the inductor-relays and the wires (or traces) interconnecting them. I'll have to see if these are an issue when I build the network.
>>> Important Note!!! <<<
Schematics will change as this design progresses.
Be sure to check later postings in this series
(especially
Part 7) for later versions.
OK -- that's it for this blog post!
The previous post in this series, Part 3, can be found here: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/06/antenna-auto-tuner-design-part-3.html
And the final "release" schematics can be found in Part 10 of this series: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2016/01/antenna-auto-tuner-design-part-10-final.html
Links to my blog posts in this Auto-tuner series:
Part 1: Preliminary Specification
Part 2: Network Capacitor Selection
Part 3: Network Inductor Selection
Part 4: Relays and L-Network Schematic (Preliminary)
Part 5: Directional Coupler Design
Part 6: Notes on Match Detection
Part 7: The Build, Phase 1
Part 8: The Build, Phase 2 (Integration of Match Detection)
Part 9: The Build, Phase 3 (Incorporating a Microcontroller)
Part 10: The Final Schematics
Resources:
- Datasheet, Relay, GR2L series, Omron: https://www.components.omron.com/components/web/pdflib.nsf/0/8F66C9A835A195FE85257201007DD572/$file/G2RL_0911.pdf
- Datasheet, Relay, ALZ series, Panasonic: http://www3.panasonic.biz/ac/e_download/control/relay/power/catalog/mech_eng_lz.pdf
- Datasheets, GDT, 1000V, EPCOS: http://media.digikey.com/pdf/Data%20Sheets/Epcos%20PDFs/B88069X3880T502.pdf
- Data, RF Breakdown Voltage, Transmitter Site Preparation Recommendations Sep 2004, Nautel: www.nautel.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/Transmitter-Site-Preparation-Recommendations-Sep-2004.pdf
- Calculator, High Voltage Gap, Cirris Systems: https://www.cirris.com/learning-center/calculators/50-high-voltage-arc-gap-calculator
My Other Tuner posts:
A quick tutorial on Smith Chart basics: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/03/a-brief-tutorial-on-smith-charts.html
The L-network: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/03/notes-on-antenna-tuners-l-network-and.html
A correction to the usual L-network design constraints: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/04/revisiting-l-network-equations-and.html
A look at highpass T-Networks: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/04/notes-on-antenna-tuners-t-network-part-1.html
More on the W8ZR EZ-Tuner: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/05/notes-on-antenna-tuners-more-on-w8zr-ez.html (Note that this tuner is also discussed in the highpass T-Network post).
The Elecraft KAT-500: http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/05/notes-on-antenna-tuners-elecraft-kat500.html
The Nye-Viking MB-V-A and the Rohde Coupler : http://k6jca.blogspot.com/2015/05/notes-on-antenna-tuners-nye-viking-mb-v.html
Standard Caveat:
As always, I might have made a mistake in my equations, assumptions, drawings, or interpretations. If you see anything you believe to be in error or if anything is confusing, please feel free to contact me or comment below.
And so I should add -- this design and any associated information is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.